In the ever-evolving world of fashion, Fabric Textile plays a pivotal role. According to a recent report by the Global Textile Industry, the market for fabric is expected to reach $1.23 trillion by 2024. This growth highlights the significance of textiles in modern design and consumer preferences. Renowned textile expert Dr. Lisa Moreau states, “The fabric we choose impacts not only style but also sustainability in fashion.”
Fabric Textile is not just about aesthetics; it encompasses sustainability and functionality. Current trends lean towards eco-friendly fabrics, reflecting changing consumer demands. Around 60% of consumers look for sustainable options when purchasing clothing. These shifts urge designers to innovate and rethink their material choices. The challenge lies in balancing style with ethical production.
Every fabric tells a story. Each choice reflects a designer’s values and vision. However, the textile industry must address the environmental impact of production. From waste to water pollution, the consequences are significant. The modern fashion landscape calls for a deeper understanding of Fabric Textile’s responsibilities. In this context, embracing sustainability is not just a trend; it is essential for long-term success.

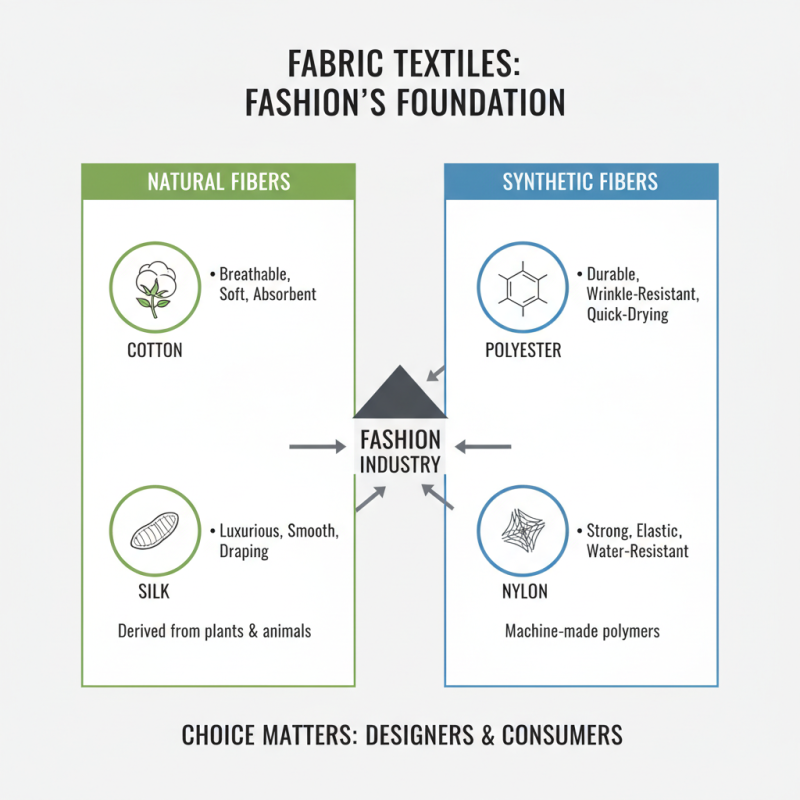
Fabric textile plays a crucial role in the fashion industry. It encompasses a wide range of materials used in clothing and accessories. There are natural fibers, like cotton and silk, and synthetic ones, such as polyester and nylon. Each fabric has its unique properties. For example, cotton is breathable, while polyester is durable. Understanding these differences is vital for designers and consumers alike.
In fashion, the classification of textiles impacts both style and functionality. Different fabrics cater to diverse needs. Some fabrics drape beautifully, while others provide structure. Textiles can also influence the environment, requiring thoughtful choices. Sustainable options are becoming increasingly popular, but not all fabrics are eco-friendly. The textile industry faces ongoing challenges regarding waste and pollution. Reflecting on these issues helps shape a better future in fashion.
Fabric textiles play a crucial role in modern fashion. They can be classified into two main categories: natural and synthetic textiles. Natural fabrics, like cotton and silk, are derived from plants and animals. They offer breathability, comfort, and a unique touch. Synthetic fabrics, such as polyester and nylon, are made through chemical processes. They are durable and resistant to wrinkles but may lack the same comfort.
When choosing fabrics, consider their use. Natural textiles are great for casual wear, while synthetics fit athletic gear. Yet, natural fabrics can require more care. They might shrink or fade over time. Synthetic options are easier to clean but might irritate sensitive skin.
**Tips:** Always check fabric labels. Knowing the composition can help you make informed choices. Consider your body type and lifestyle when selecting textiles. Quality matters, so sometimes, spending a little more helps in the long run. Remember that not all fabric blends work well for everyone. Experimenting can lead to surprising finds!
Fabric textiles play a crucial role in fashion design and production processes. They define the overall aesthetic of a collection. The texture, durability, and drape affect how designs emerge from sketches. Designers select fabrics that enhance their vision. Cotton, silk, and denim each tell a different story. The choice affects price points too. Many tend to overlook how fabric influences sustainability.
In production, fabric selection is often rushed. This can lead to poor quality garments that harm brand reputation. Workers often feel pressure to meet tight deadlines. Sometimes, they sacrifice quality for speed. Mistakes happen. It's essential to balance efficiency and craftsmanship. Mistakes in fabric sourcing can lead to waste. Designers grapple with sourcing ethical materials while being budget-conscious.
The relationship between fabric and design is intricate. Sometimes, it’s not just about the look but also the feel. Fabrics evoke emotions. A soft silk may feel luxurious, while a sturdy canvas can be practical. Designers must navigate these feelings closely. The role of fabric textiles is, thus, both vital and complex in modern fashion, calling for deeper reflection.

The global fashion market heavily relies on fabric textiles. These materials shape the industry’s aesthetic and functional aspects. Various fabrics influence trends and styles, creating endless possibilities for designers. The economic impact is significant. Research shows that textiles contribute billions to the global economy. They employ millions worldwide. This industry spans from fiber production to garment manufacturing.
In many regions, textiles drive local economies. They foster entrepreneurship and craft traditions. However, the industry faces challenges. Sustainability is a pressing issue. Fast fashion often leads to waste and environmental harm. Consumers are becoming more aware. They demand eco-friendly options. This shifts market dynamics and challenges established practices.
**Tip:** Consider the origin of your fabric. Ethically sourced materials can boost local economies.
Innovation plays a crucial role in this sector. Advances in technology improve production efficiency. However, over-reliance on technology risks job losses in traditional crafts. Striking a balance is essential for growth.
**Tip:** Explore brands that prioritize sustainable practices. They often support fair labor conditions.
Textiles reflect culture and identity. They tell stories through patterns and textures. As the market evolves, so must our understanding of fabric's role in economy and society.
Sustainability in fabric textiles is gaining traction. The fashion industry is making notable strides. Innovations are emerging to address environmental challenges. According to a recent report, the textile industry accounts for nearly 10% of global carbon emissions. This statistic highlights the urgent need for sustainable practices.
Recycled materials are at the forefront of this movement. Brands are exploring alternatives like recycled polyester and organic cotton. These materials require less water and energy than traditional fabrics. However, the challenge remains in scaling these innovations. A significant portion of the industry still relies on conventional methods. This resistance to change can impede progress.
Consumer awareness is growing. Shoppers are becoming more conscious of their choices. They demand transparency and ethical sourcing. However, not all brands adhere strictly to these principles. The gap between consumer expectations and industry actions is concerning. Further education and regulatory measures are needed to bridge this divide. Balancing fashion trends with sustainability is a complex task.