Textile wax is a versatile and essential component in the world of fabric treatments, providing not only a protective barrier but also enhancing the aesthetic appeal of various textiles. As the demand for durable and functional fabrics grows, the application of textile wax has become increasingly popular among manufacturers and consumers alike. This innovative substance modifies the properties of fabrics, rendering them water-resistant, stain-repellent, and more resilient to wear and tear, thus extending their lifespan and maintaining their appearance.
In addition to its protective qualities, textile wax offers unique opportunities for creative expression within fashion and design. By adding depth and texture, it allows designers to experiment with the tactile qualities of their fabrics, fostering originality and innovation. Moreover, the application methods of textile wax can vary, leading to exciting possibilities in both handmade and industrial processes. As we delve deeper into the world of textile wax, we will uncover its composition, various applications, and the impact it has on contemporary fabric treatments, illuminating why it has become a pivotal element in fabric care and enhancement.
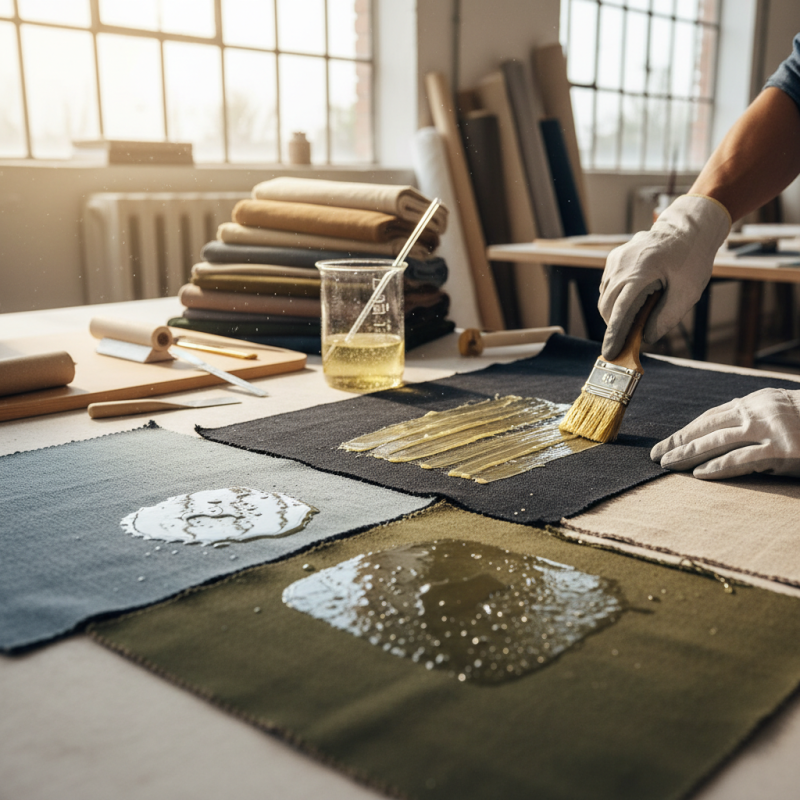

Textile wax is a specialized substance used in the treatment of fabrics, designed to enhance their durability and performance. It is typically composed of a blend of natural and synthetic waxes, which may include paraffin, beeswax, and carnauba wax, among others. These components contribute to the wax's unique properties, such as water repellency, stain resistance, and flexibility, making it an ideal choice for treating various textile materials.
The primary function of textile wax is to create a protective barrier on the fabric surface. When applied, it penetrates the fibers, improving the fabric's resistance to moisture and dirt. This not only extends the lifespan of the textile but also enhances its aesthetic appeal by maintaining color and texture. The composition of textile wax can be tailored to meet specific application needs, whether for outdoor gear, upholstery, or fashion fabrics, ensuring that different textiles receive the optimal protection and functionality required in their respective uses.
Textile wax is essential in the treatment of fabrics, providing both protection and aesthetic qualities. There are various types of textile wax available, each serving distinct purposes in the textile industry. One of the most common types is paraffin wax, known for its ease of application and effectiveness in providing water resistance. It is often used in outdoor apparel and gear, ensuring that fabrics maintain their functionality in wet conditions.
Another significant type is beeswax, which is renowned for its natural properties and environmental benefits. This wax not only offers water-repellent qualities but also enhances the longevity of the fabric, making it ideal for items that undergo heavy usage, such as bags and shoes. Additionally, soy wax is gaining popularity among eco-conscious producers, as it is a renewable resource that provides a soft finish and a pleasant aroma. Each type of textile wax contributes uniquely to fabric treatments, catering to diverse needs while upholding sustainability standards in fabric care.
| Type of Textile Wax | Composition | Common Uses | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paraffin Wax | Hydrocarbon mixture | Waterproofing, softeners | Low cost, easy to apply |
| Beeswax | Natural wax from honeycombs | Water resistance, fabric conditioning | Natural, eco-friendly, antimicrobial |
| Microcrystalline Wax | Synthetic wax with fine crystals | Textile finishes, waterproofing | Flexibility, high adhesive properties |
| Carnauba Wax | Plant-based wax | Finishing, shine enhancement | Natural luster, durability |
| Synthetic Wax Blends | Various synthetic polymers | Textile treatments, finishes | Versatile, tailored properties |
Textile wax is commonly used to enhance the protective qualities of fabrics, making garments more resistant to water and stains. Its application can vary widely, but several methods stand out for their effectiveness.
One popular technique is the direct application of melted wax onto the fabric, where it is brushed or spread evenly across the surface. This method allows for a thick, protective layer to be formed, ideal for outdoor gear and garments that require extra durability.
Another application method involves using a wax-infused spray or solution, which can be easily applied to the fabric. This technique is advantageous for achieving a more uniform coverage without altering the texture of the fabric significantly. After spraying, the fabric is typically heat-treated with an iron or left to air dry, which helps the wax bond effectively to the fibers, ensuring lasting protection against environmental elements.
Each of these methods offers unique benefits, making textile wax a versatile solution in the realm of fabric treatments.
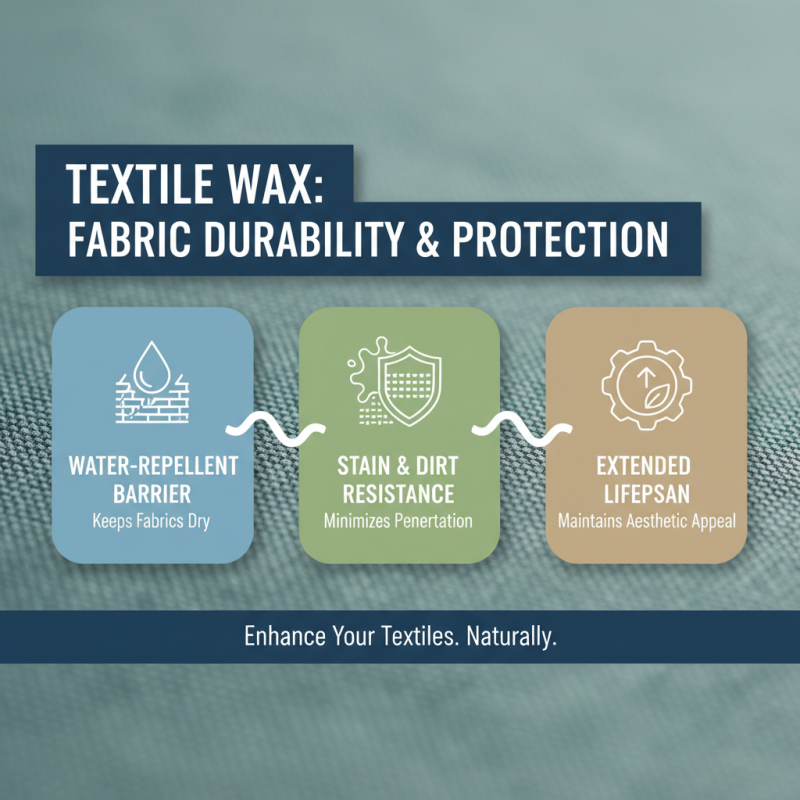
Textile wax is an increasingly popular solution for enhancing fabric durability and protection. One of the key benefits of using textile wax in fabric treatments is its ability to create a water-repellent barrier. This barrier not only helps to keep fabrics dry but also minimizes the penetration of stains and dirt. As a result, textiles treated with wax can maintain their aesthetic appeal and last longer, even in challenging environments.
In addition to water resistance, textile wax can enhance breathability in fabrics. Unlike some synthetic treatments that may trap heat and moisture, textile wax permits airflow while still providing effective protection. This characteristic is especially beneficial for outdoor gear and clothing, where moisture management is crucial.
**Tips for using textile wax effectively:** First, ensure that the fabric is clean and dry before applying the wax for optimal adhesion. When applying, use a soft cloth or sponge to evenly distribute the wax, focusing on seams and areas prone to wear. Lastly, consider reapplying the wax periodically, especially after washing, to maintain the protective qualities of the fabric.
The use of textile wax in fabric treatments involves several environmental considerations that are paramount in today’s sustainability-focused landscape. Textile waxes often derived from natural sources, such as plant-based waxes, offer a more eco-friendly alternative to synthetic coatings. The production and application of these natural waxes tend to have a lower carbon footprint compared to their synthetic counterparts. Additionally, they are biodegradable, which means they break down more easily in the environment, reducing the long-term impact on ecosystems.
However, it is important to consider sourcing and production practices. The extraction of materials for natural waxes can lead to environmental degradation if not managed sustainably. Responsible sourcing practices are essential to ensure that the benefits of using natural textile wax do not come at the expense of deforestation or harm to wildlife habitats. Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on the development of closed-loop systems in textile processing, which can minimize waste and encourage the reuse of materials.
Balancing the benefits of natural textile wax with these environmental considerations is crucial for achieving truly sustainable fabric treatments in the fashion and textile industry.






